Powering India’s Energy Future: The Role of AI in Transforming the Power Grid
India’s energy sector continues to advance rapidly as the country strives to meet its ambitious targets for sustainable development and net zero emissions by 2070. The drive to achieve a non-fossil fuel energy capacity of 500 GW by 2030 under the Paris Agreement has intensified, requiring significant modernization of the nation’s power grid to manage the complexities introduced by renewable energy sources.
To address the challenges of integrating renewables, Indian grid operators are increasingly leveraging artificial intelligence (AI) to enhance grid management, stability, and reliability. As of 2024, AI technologies have become vital for facilitating real-time data analysis, predictive capabilities, and automated decision-making to support the world’s third-largest power grid serving over 1.4 billion people.
In this article we will explore the role of AI in transforming the power grid of India.
How AI Is Transforming Grid Management in India
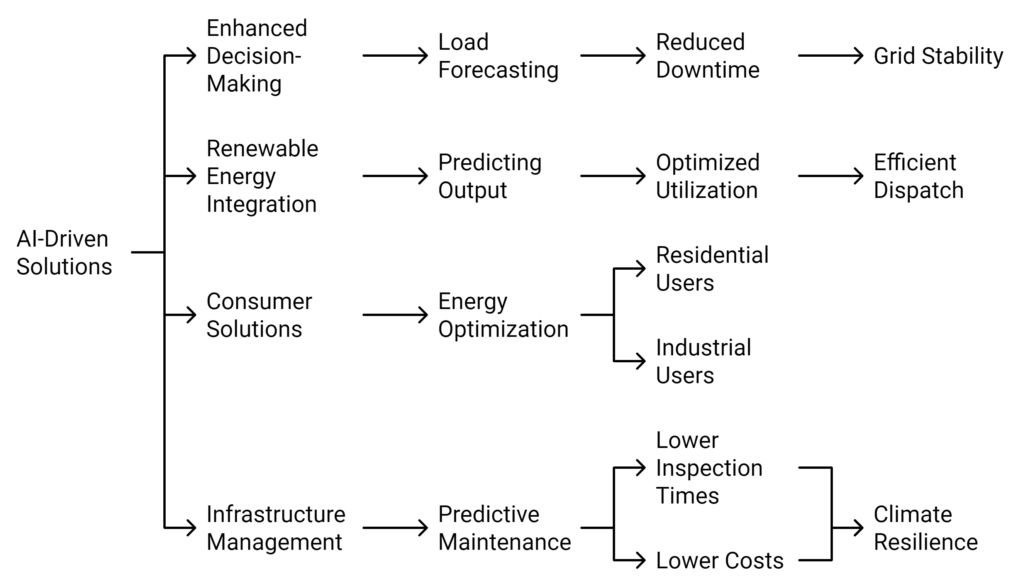
Enhanced Decision-Making and Predictive Analysis India’s power grid, comprising more than 420,000 circuit kilometers of transmission lines and approximately 415 GW of installed capacity (as of August 2024), faces persistent challenges in balancing supply and demand. AI-driven solutions are now integral to maintaining real-time grid balance through predictive analytics, automated monitoring, and efficient dispatching.
Grid Controller of India Ltd (formerly POSOCO) has expanded its use of AI tools to include more advanced load forecasting models. These models analyze historical consumption data, weather forecasts, and socio-economic trends to predict demand with high accuracy. This helps in scheduling energy dispatches efficiently and mitigating risks of blackouts. AI algorithms have reduced downtime by approximately 25% since their adoption, significantly enhancing grid stability.
Optimizing Renewable Energy Integration India’s renewable energy capacity has reached over 150 GW, with solar energy contributing about 80 GW and wind power approximately 46 GW as of 2024. Achieving the 500 GW target by 2030 will require sophisticated systems to manage the intermittency of renewables. AI-driven solutions are enabling this by integrating data from weather monitoring stations, satellite feeds, and on-ground sensors to predict renewable energy output accurately.
Tata Power and NTPC Limited have scaled up the deployment of AI-enhanced energy management systems. NTPC’s recent projects demonstrate that AI can boost renewable energy utilization rates by as much as 25%, ensuring optimal dispatch and minimizing the impact of energy variability on the grid.
Personalized Consumer Solutions AI applications in energy management have expanded to residential and commercial users. Luminous Power Technologies’ AI-driven platforms now provide enhanced solutions that monitor and adjust solar panel outputs and battery storage for homeowners, leading to greater energy savings and reduced dependency on the grid. Similarly, Amplus Solar has broadened its AI-powered services to industrial clients, offering advanced analytics for energy optimization that align with peak demand management.
AI-Driven Electric Vehicle (EV) Integration India’s electric vehicle market has surged, with over 2.5 million EVs on the road by August 2024. The expansion has been supported by government incentives, an increase in EV infrastructure, and public awareness. Managing this growth, particularly in urban centers, has posed new challenges to the power grid.
Tata Power’s EZ Charge platform remains at the forefront of AI-driven load management, enabling synchronized EV charging that balances grid load during peak and off-peak periods. The platform has expanded to include machine learning models that predict high-usage times and adjust charging schedules accordingly. Fortum India’s collaboration with leading utility companies has also seen progress, with AI-based charging solutions aligning charging operations with high renewable energy generation periods, thereby reducing grid strain and supporting lower emissions.
Proactive Infrastructure Management Extreme weather events continue to threaten the reliability of India’s power infrastructure. The Power Grid Corporation of India Limited (PGCIL) has broadened its use of AI in predictive maintenance, employing IoT sensors, drones, and advanced machine learning algorithms for continuous monitoring. By 2024, PGCIL has reported that AI has reduced the time needed for transmission line inspections by up to 45% and lowered maintenance costs substantially.
Adani Electricity Mumbai Limited and other private utilities have integrated AI for risk management, enhancing the resilience of their transmission and distribution systems.
Climate Risk Management Climate change remains a pressing issue for India’s energy sector. AI platforms developed by Climate Connect Technologies are playing a pivotal role in predictive modeling to foresee and prepare for extreme weather events. These platforms incorporate climate forecasts and grid data to inform strategies for strengthening infrastructure against potential damage, ensuring faster recovery post-disruption.
The Ministry of Power’s ongoing emphasis on climate resilience has led to more robust AI-driven risk assessment frameworks that forecast potential grid failures and suggest preemptive measures.
Aligning with India’s Net Zero Targets
To reach net zero by 2070, AI is indispensable for transforming grid operations and enhancing energy efficiency. The International Energy Agency (IEA) notes that AI-optimized grids can reduce operational emissions by up to 20% by 2030, contributing significantly to India’s climate targets.
The Central Electricity Authority (CEA) continues to work closely with the Ministry of Power to facilitate the adoption of smart grid technologies. Policy support now includes incentives for AI-based grid enhancements, ensuring that all stakeholders, from public to private sectors, align with national energy and climate goals.
Challenges and Future Prospects
While AI integration has shown promising results, challenges persist. The vast amount of data required for effective AI modeling raises concerns over data privacy and cybersecurity. The Indian government is addressing these issues through frameworks such as the Digital Personal Data Protection Bill, which outlines standards for data handling and security.
Ensuring equitable access to AI technologies, particularly in rural areas, remains an area of focus. The push for inclusive AI adoption calls for investment in training programs and public-private partnerships to equip the workforce with relevant skills.
Moving Forward
AI is revolutionizing India’s power grid, fostering a more efficient, resilient, and adaptive infrastructure that supports the country’s energy transition. By facilitating smarter grid management, enhancing renewable energy integration, and building climate resilience, AI is pivotal in India’s journey to a net zero future. The successful realization of these benefits will rely on continuous policy support, robust data governance, and inclusive technological dissemination across all sectors of society.
This approach will help India achieve its climate commitments and ensure a sustainable, energy-secure future for its vast population.

